

The standard error of the math scores, on the other hand, tells you how much the sample mean score of 550 differs from other sample mean scores, in samples of equal size, in the population of all test takers in the region. This number reflects on average how much each score differs from the sample mean score of 550. The standard deviation of the math scores is 180. In this case, the sample is the 200 students, while the population is all test takers in the region. Example: Standard error vs standard deviationIn a random sample of 200 students, the mean math SAT score is 550. In contrast, the standard error is an inferential statistic that can only be estimated (unless the real population parameter is known). The standard deviation is a descriptive statistic that can be calculated from sample data. The standard error estimates the variability across multiple samples of a population.The standard deviation describes variability within a single sample.Standard error and standard deviation are both measures of variability: Using a large, random sample is the best way to minimize sampling bias. You can decrease standard error by increasing sample size. A low standard error shows that sample means are closely distributed around the population mean-your sample is representative of your population. That’s because a sample will never perfectly match the population it comes from in terms of measures like means and standard deviations.īy calculating standard error, you can estimate how representative your sample is of your population and make valid conclusions.Ī high standard error shows that sample means are widely spread around the population mean-your sample may not closely represent your population. With probability sampling, where elements of a sample are randomly selected, you can collect data that is likely to be representative of the population. However, even with probability samples, some sampling error will remain. Standard error matters because it helps you estimate how well your sample data represents the whole population. In statistics, data from samples is used to understand larger populations. Frequently asked questions about standard error.

How should you report the standard error?.Your thoughts on this matter would be really appreciated. It would not only provide the standard error and the t-statistic, but also allow me to export the results to LaTex.
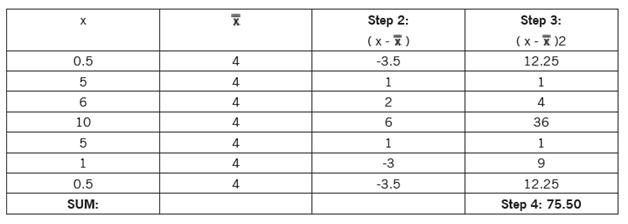
#HOW TO CALCULATE STANDARD ERROR HOW TO#
As such, ideally I would like to run a 2sls with covariates and get the same coefficient as I would using method one, but don't know how to code it. I wrote to the writter of the fuzzydid command who informed me that their command includes the covariates more flexibly, allowing to vary over time and between groups as opposed to the linear regression with covariates where the coefficients are the same for both groups and time periods. However, when including covariates, the two methods differ. When using method 1 and 3, I get the same coefficients, with method 3 providing me with the standard error and t-statistics (though there are not included in the ereturn list, so I am still struggling to export them). Code: fuzzydid service_satisfaction dist_intervention1 survey_year property_demand, did****


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
